What is Riboflavin?
Riboflavin is also known as vitamin b2, with the CAS No.83-88-5. As a supplement it is used to prevent and treat riboflavin deficiency and prevent migraines. It can be used as an deep yellow – orange – red food colouring with the E number E101. Riboflavin can also be used as a food and feed additive. When used to fortify foods, typical products include cereals, sauces, vitamin supplements, soups.
Vitamin B2 Riboflavin Property
Appearance
It is a yellow or orange yellow crystalline powder; smells slightly bitter; Slightly dissolves in water, not dissolve in ether, alcohol and chloroform, with the melting point of 281-290℃.
Riboflavin solubility
It is water soluble, but lower water solubility than other B vitamins.
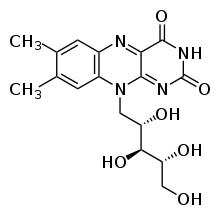
Chemical formula of riboflavin
C17H20N4O6
Molecular weight
376.37 g·mol−1
Chemical structure
Riboflavin assay
The assay depends on it is food/pharma/feed grade,
- Food/pharma grade: BP/USP/EP/FCC, 100%
- Feed grade: 80%
Riboflavin (vitamin B2) is very stable during thermal processing, storage, and food preparation. Riboflavin, however, is susceptible to degradation on exposure to light. The use of light-proof packaging material prevents its deterioration.
Vitamin B2 Riboflavin in milk
Milk is the good source of Riboflavin and high with it. Milk contains the water soluble vitamins thiamin (vitamin B1), riboflavin (vitamin B2), niacin (vitamin B3), pantothenic acid (vitamin B5), vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), vitamin B12 (cobalamin), vitamin C, and folate. Milk is a good source of thiamin, riboflavin and vitamin B12 . Milk contains small amounts of niacin, pantothenic acid, vitamin B6, vitamin C, and folate and is not considered a major source of these vitamins in the diet.
Vitamin B2 Riboflavin and pregnancy
Why you need riboflavin during pregnancy. Riboflavin, or vitamin B2, is an essential vitamin that helps your body produce energy. It promotes your baby’s growth, good vision, and healthy skin. Riboflavin is also essential for your baby’s bone, muscle, and nerve development.
Reference: https://www.babycenter.com/0_riboflavin-in-your-pregnancy-diet_672.bc
Source of riboflavin: Meat products, vegetables and fruits
Riboflavin is found in a wide variety of foods. Enriched grains are good sources of riboflavin. Quinoa and some fruits and vegetables also contain rich riboflavin. Foods source such as seafood, lean meats and poultry, eggs, legumes (beans and peas), nuts, seeds, and soy products. Almonds, beef and lamb, Oily fish, egg, pork, mushrooms, sesame seeds, seafood, spinach.
This following table will show you sources of riboflavin. Milk and dairy products are the richest sources.
| Food | Serving Size | Riboflavin (mg) |
| Vegetables and Fruits | ||
| Vegetables | ||
| Mushroom (white, portabello, crimini), raw or cooked | 125 mL (½ cup) | 0.2-0.6 |
| Spinach, cooked | 125 mL (½ cup) | 0.2 |
| Grain Products | ||
| Cereal, corn flakes | 30 g (check product label for serving size) | 1.1 |
| Cereal, muesli | 30 g (check product label for serving size) | 0.2 |
| Waffle | 1 small (35g) | 0.2 |
| Milk and Alternatives | ||
| Milk (3.3% homo, 2%, 1%, skim) | 250 mL (1 cup) | 0.4-0.5 |
| Cottage cheese | 250 mL (1 cup) | 0.4-0.6 |
| Buttermilk | 250 mL (1 cup) | 0.4 |
| Cheese, feta | 50 g (1½ oz) | 0.4 |
| Yogurt beverage | 200 mL | 0.4 |
| Yogurt (fruit, plain, Greek), all types | 175 g (¾ cup) | 0.2-0.4 |
| Soy beverage | 250 mL (1 cup) | 0.4 |
| Cheese (cheddar, monterey, edam, colby, blue, brie, camembert) | 50 g (1½ oz) | 0.2 |
| Ricotta cheese | 125 mL (½ cup) | 0.2 |
| Meat and Alternatives | ||
| Meat | ||
| Pork, various cuts, cooked | 75 g (2½ oz) | 0.2-0.3 |
| Beef, various cuts, cooked | 75 g (2½ oz) | 0.2-0.3 |
| Chicken or turkey, dark meat, cooked | 75 g (2½ oz) | 0.2 |
| Organ Meats | ||
| Liver (chicken, turkey, pork, beef), cooked | 75 g (2½ oz) | 1.6-2.7 |
| Fish and Seafood | ||
| Cuttlefish, cooked | 75 g (2½ oz) | 1.3 |
| Salmon, cooked | 75 g (2½ oz) | 0.4 |
| Mackerel, cooked | 75 g (2½ oz) | 0.3-0.4 |
| Squid, cooked | 75 g (2½ oz) | 0.3 |
| Trout, cooked | 75 g (2½ oz) | 0.3 |
| Shellfish (clams, mussels), cooked | 75 g (2½ oz) | 0.2-0.3 |
| Herring, cooked | 75 g (2½ oz) | 0.2 |
| Sardines, canned in oil | 75 g (2½ oz) | 0.2 |
| Meat Alternatives | ||
| Vegetarian meatloaf or patty, cooked | 75 g (2½ oz) | 0.5 |
| Tempeh/fermented soy product, cooked | 150 g (3/4 cup) | 0.5 |
| Egg, cooked | 2 large | 0.4-0.5 |
| Almonds, without shell | 60 mL (¼ cup) | 0.3-0.4 |
| Soy nuts | 60 mL (1/4 cup) | 0.2 |
| Meatless, chicken, cooked | 75 g (2½ oz) | 0.2 |
| Other | ||
| Yeast extract spread (marmite or vegemite) | 30 mL (2 Tbsp) | 5.3 |
Vitamin B2 Riboflavin absorption, metabolism and pathway
Most of the vitamin B2 in the diet is present as a combination of flavin mononucleotide (FMN) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) with proteins. The metabolism begins after it enters into the stomach, it is separated with the protein by the function of stomach acid and become the free Vitamin B2. It is absorbed in the upper part of the small intestine after go through the upper gastrointestinal tract. If the intake of Vitamin B2 is large, the liver and kidney often have higher concentrations, but the body’s ability to store vitamin B2 is limited. The part exceeds the renal threshold will passes through the urinary system and excrete in a free form. This is the pathway. Therefore, the daily needs of Vitamin B2 must be from the diet.
Vitamin b2 Riboflavin deficiency symptoms
Vitamin B2 deficiency is rare as this vitamin is found in almost all common foods, still it can occur in people who are under weight, those who have frequent digestive problems or in adolescent girls who avoid milk and rarely have vegetables.
Vitamin B2 (VB2), is a water-soluble vitamin but has low water solubility, is stable under acidic conditions, is unstable under alkaline conditions, and can be decomposed when exposed to light.
It is involved in the redox reaction and energy production in the body in the form of coenzymes. It is closely related to the body’s antioxidant defense system. It plays an important role in the metabolism of amino acids, fatty acids and carbohydrates. It also participates in the metabolism of vitamin B6, niacin and some drugs, and it is related to the absorption and storage of iron in the body. It is also an important nutrient for maintaining good health.
Vitamin B2 deficiency is a relatively common nutritional deficiency disease, and its performance mainly has three symptoms: lip damage, rotten mouth, hair loss, Skin lesions, loss of sleep, lip and tongue inflammation, can form a “map tongue.” Seborrheic dermatitis often occurs on both sides of the face’s nose, between the forehead and the two eyebrows, and males can develop scrotal eczema-like dermatitis.
Women occasionally have cheilitis. There are eye symptoms, the performance of blurred vision, photophobia, tears, collectively referred to as “oral reproductive syndrome.” As the deficiency coexistence with other B vitamins, the diagnosis of Vitamin B2 deficiency may not be easy. Insufficient supply of VB2 in the general diet lasts for 3-4 months and symptoms can appear. The lack of VB2 can interfere with the absorption, storage, and mobilization of iron in the body, it can result in a decrease in the content of iron in the body, and therefore anemia may occur.
The deficiency of Vitamin B2 can be diagnosed by asking patients the food eating habits and experimental treatment methods. If necessary, laboratory tests such as urinary riboflavin test can be performed, but it is generally not easy to do.
The main reasons for the Vitamin B2 deficiency are insufficient intake, ingestion of foods containing little VB2, and unreasonable storage and cooking methods, so VB2 is destroyed or lost. For example, the over-processing of rice or flour can lead to the loss of nutrients. VB2 can be destroyed during repeated heating of milk and food heating and exposure to sunlight. Deep-fried foods can destroy VB2 up to 50%. Adding alkali can cause VB2 to be destroyed in large quantities. Digestive system diseases such as long-term diarrhea, intestinal resection, and low gastric acid levels can affect the absorption of VB2.
The need of VB2 increases during the time of pregnancy, breast-feeding, heavy physical labor, high fever, etc.,. If it is not supplemented in time, it can easily lead to a deficiency of VB2. Alcoholics are also prone to VB2 deficiency due to alcohol interference in the digestion and absorption of VB2. Due to the low solubility of VB2 in water, the body’s absorption is also limited. Ingestion of VB2 in large amounts does not increase the absorption of intestinal tract indefinitely. Excessive VB2 can be excreted in the urine, so there is no report of VB2 poisoning.
VB2 is widely found in animal and plant foods. The source in animal organs, eggs, and milk are relatively high. Green leafy vegetables and legumes contain more VB2 in plant foods, and cereals have lower content.
In order to avoid VB2 deficiency, we should pay attention to eating more foods rich in VB2, correcting poor dietary habits of partial eclipses, not eating too much processed grains, paying attention to coarse grains, and improving cooking methods to reduce the loss of VB2. For pregnant women, nursing mothers, children and heavy manual workers should pay attention to increase their intake of VB2 and take certain animal foods high with VB2 every day.
Vitamin b2 riboflavin active form
The active forms (the forms in which the body uses them) of Riboflavin are synthesised in the mitochondria, forming Riboflavin 5 Phosphate which is then converted further to Flavine Adenine Dinucleotide (FAD) Metabolics Vitamin B2 is in its bioavailable form Riboflavin 5 phosphate.
Riboflavin is the essential necessity for organism in normal living as the nutriment for infant, pregnant woman nursing mother, patient after illness and the aged. It, involve , participates in the metabolishm of carbonhydrate, protein and fat, and is the major composition of flavorprotein, the transferring enzyme system of hydrogen, In clinical practice, it is applicable to perleche, glossitis, ophthalmitis, conjunctivitis, ceborrhea, scrotum inflammations with proper effect ,In food and feed industry, it is widely used as food and feed additives
Is Vitamin B2 riboflavin vegan?
Vegans care about the food they eat. They are dedicated to avoiding animal mistreatment and cruelty. For these reasons, vegans, to the best of their ability, reject eating animals or anything containing animal products, like Meat, fish, seafood, dairy, honey and eggs. However, while avoiding animal-based food, a vegan has to face with taking nutritional supplements.
As Vitamin B2 is high both in animal products also in fruit and vegetables, a vegan can eat fruit and vegetables rich with Vitamin B2.
Vitamin b2 riboflavin Function
What does riboflavin do and the function in the body
- Energy metabolism – Vitamin B2 is required in its coenzyme form (FAD) for participation in the Citric Acid cycle to produce energy.
- Functioning of the nervous system- Vitamin B2 is needed for the monoamine oxidase enzyme, which functions in the metabolism of neurotransmitters ( brain chemicals ) for normal functioning of the nervous system.
- Maintenance of normal red blood cells- Vitamin B2 improves iron absorption and riboflavin deficiency induces anaemia , where there are immature red blood cells.
- Maintenance of normal skin and mucous membranes–both acute and chronic deficiencies result in mucocutaneous lesions that disappear after adequate doses of B2 are given.
- Maintenance of normal vision- Riboflavin deficiency is associated with decreased activity of the enzyme glutathione reductase, the enzyme responsible for the production of glutathione. Reduced glutathione protects the lens of the eye from oxidative damage and is decreased in cataracts. Riboflavin deficiency can cause conjunctivitis with vascularisation of the cornea and opacity of the lens (cataracts).
- Metabolism of iron. Iron metabolism is impaired in riboflavin deficiency. The utilization of iron reserves from the intracellular protein ferritin requires riboflavin. Riboflavin is required for haemoglobin synthesis.
- Protection of cells from oxidative stress. Vitamin B2 participates in many reactions where the cofactors P-5-P and FAD act as electron carriers, protecting the DNA, proteins and lipids from oxidative damage.
- Reduction of tiredness and fatigue. As Vitamin B2 is involved in manufacturing energy adequate doses of B2 contribute to normal metabolism resulting in energy.
Benefit for headaches
Besides the above benefits, Riboflavin is also helpful for headaches.
A few studies in adults show that riboflavin (vitamin B2) might decrease frequency of migraine headaches. It has become common practice to recommend that children try riboflavin to prevent migraine; however, research on riboflavin use in children is inconclusive.
Reference: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3952759/
What does vitamin b2 riboflavin prevent
It can prevent following or more disease and symptoms caused by deficiency of vitamin b2 riboflavin:
- Weakness
- Hair loss
- Skin lesions
- loss of sleep
- Throat swelling/soreness
- Swollen tongue
- Skin cracking (including cracked corners of the mouth)
- Dermatitis
- Anaemia
- Blurred vision and itching, watering, sore, or bloodshot eyes
- Eyes becoming light-sensitive and easily fatigued
Vitamin b2 riboflavin Side effects
Most people tend to tolerate riboflavin very well. You might notice your urine taking on a bright yellow color.
Too much riboflavin
Too much intake of Riboflavin may cause itching, paralysis, nosebleeds, burning sensation, tingling, etc. If you are taking anticancer drugs such as methotrexate, excessive B2 will reduce the effectiveness of these anticancer agents.
Riboflavin toxicity
Although the amounts of vitamin B2 found in multivitamin supplements and in your diet don’t pose any risks of toxicity, the therapeutic dosages could provide excessive amounts of riboflavin, according to the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center. Despite the large amounts, vitamin B2 appears to be very safe, however. Even at extremely high doses, vitamin B2 rarely causes side effects, much less toxicity, notes the University of Maryland Medical Center. Reported side effects from taking more than 10 mg per day of riboflavin include sun-induced eye damage, itching or numbing sensations, and orange-tinted urine.
Reference: https://www.livestrong.com/article/274360-vitamin-b2-toxicity/
What is Riboflavin 5′ phosphate sodium
Riboflavin 5′-Phosphate Sodium is the phosphate sodium salt form of riboflavin, a water-soluble and essential micronutrient that is the principal growth-promoting factor in naturally occurring vitamin B complexes.
It is also called riboflavin 5 phosphate, RIBOFLAIVN 5’ SODIUM PHOSPHATE, VITAMIN B2 5’ PHOSPHATE SODIUM, riboflavin 5 monophosphate, riboflavin 5, vitamin b2 5 phosphate
CAS No. 130-40-5
Chemical Formula: C17H20N4NaO9P · 2H2O
Molecular weight: 514.36
Riboflavin 5′-Phosphate Sodium Property
An orange yellow crystalline powder; almost odorless and tastes slightly bitter; being wet-ejection, dissolves in water easily, but slightly in ethanol and hardly dissolves in chloroform and or in ether
Having the same actions as Vitamin B2, being better than Vitamin B2 is that is easier to dissolves in water and to be absorbed and offers a high intracorporeal usage rate. More noted medical effect comes into being while it is applied to disorder of some organic functions such as failing liver function and phosphoryl impediments out of intestinal diseases. Also it can be used as preparative for stable, highly densed and active Vitamin B2 injection, Vitamin B complex agent and eye ointment and acts as additives in food and beverage.
Riboflavin 5′-Phosphate Sodium Specification
BP/USP/EP/JP/FCC
Assay 75-80%
Application
Food and Pharma industries – use in multivitamin products
Premixes – Poultry feed premixes
As a food colour
Storage
In well Sealed Containers, Stored in Cool ,dry place and keep from light.
Vitamin B2 Riboflavin and Riboflavin 5′ Phosphate Sodium Market
Vitamin B2 Riboflavin and Riboflavin 5′ Phosphate Sodium manufacturers
China is the big food and feed grade Vitamin B2 Riboflavin and Riboflavin 5′ Phosphate Sodium manufacturers and export country in the world.
Demand and supply structure: The downstream mainly consists of animal feed and food additives, which account for 64% and 32%, respectively, while pharmaceuticals and other needs are small (<5%). Feed grade VB2 powder, the assay is 80%, the food grade is mainly used as an additive in flour, energy drinks and other foods. The total demand of the global VB2 market is about 7,000 tons, and the annual demand in the domestic market is about 2,000 tons.
Manufacturing process: VB2 production process is through microbial fermentation production. At present, vitamin B2 is industrially produced by microbial fermentation in China and abroad. The microorganisms that can produce vitamin B2 are bacteria, fungi, and molds, and the industrial production mainly uses Eremotherecium ashbyii as a strain. The industrial fermentation of vitamin B2 is generally a secondary fermentation, and the fermentation liquid is first precipitated and then oxidized to separate and purify. Corn is the main raw material for the production of VB2, which accounts for more than 50% of production costs. The world’s major manufacturers include Guangji, BASF and DSM. The three companies account for more than 80% of the total capacity.
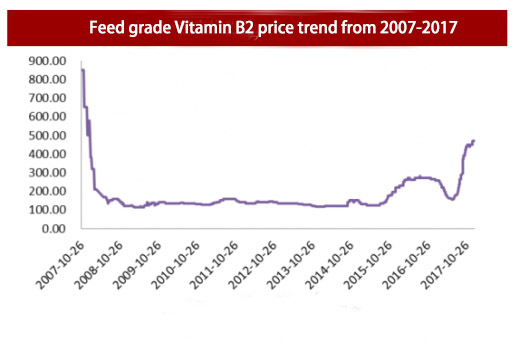
In 2016, due to the entry of new factory, the price trend was relatively sluggish. In July of 2017, manufacturers gradually entered the high-temperature maintenance period. In addition, strict inspection of environmental protection in Shandong Province, the supply of vitamin B2 contracted. During the same period, the volume of exports also began to increase significantly. The supply and demand relationship in the industry changed, prices started to rise and prices have been rising. At present (Nov, 2016), the price of vitamin B2 is about 450 yuan/kg, which is 181% higher than the 160 yuan/kg at the end of June. Follow-up With the advent of the heating season, supply may further shrink, and then superimposed on the rebound in international market exports, prices are expected to continue rising in the fourth quarter.
There are several Vitamin B2 Riboflavin and Riboflavin 5′ Phosphate Sodium manufacturers in China and abroad, as you know, the price of China suppliers can be better than abroad manufacturers. We have worked with China top manufacturer for years, we would like to recommend our selected Vitamin B2 Riboflavin and Riboflavin 5′ Phosphate Sodium manufacturers to you if you would like to save your purchasing cost with the same quality compared with abroad manufacturers. Samples are available if you need it for further test.
Today’s Vitamin B2 Riboflavin price
Updated on 2018/05/26: Now the price for feed grade 80% is around RMB125/kg, the price in January was around RMB480/kg, it decreased around 75%.
Where to buy Vitamin B2 Riboflavin and Riboflavin 5′ Phosphate Sodium?
You can buy food or feed grade Vitamin B2 Riboflavin and Riboflavin 5′ Phosphate Sodium from us, Specification complies with BP/USP/EP/JP/FCC standard.
We’re committed to the quality and safety of our ingredients. We know that our customers expect us to use only the highest quality food additives & ingredients with better price, and we do everything we can to satisfy those expectations.
If you have any other questions, please email us through: info@foodsweeteners.com