What Is Vitamin B12 Cyanocobalamin?
Cyanocobalamin, also called cobalamin, is a synthetic form of Vitamin B12. Cyanocobalamin is used to treat Vitamin B12 deficiency in people (also in animals) with pernicious anemia and other conditions. As cyanocobalamin contains cyanide, it can not be used directly in the body and must be broken down and converted into methylcobalamin and adenosylcobalamin.
Cyanocobalamin is commonly used and found in vitamins and dietary supplements manufacturing for its lower cost among other 4 types of vitamin b12. It is not naturally occurring and can only be manufactured through chemical synthesis.
Four types of Vitamin B12
There are four types of Vitamin b12: Cyanocobalamin, Hydroxocobalamin, Adenosylcobalamin and Mecobalamin. Cyanocobalamin is the only type that contains metallic elements.
Four types all have the same function – prevent and treat megaloblastic anemia & peripheral nerve diseases.
The human body can only use Methylcobalamin and Adenosylcobalamin directly, which are two active coenzyme forms of vitamin B12 in the body. Another two cobalamins must be converted into these two forms first and then can be utilized.
Let’s see the details:
1. Cyanocobalamin
It is dark red crystals or crystalline powder. It functions after converted into methylcobalamin and adenosylcobalamin in the body. Its stability is the best among the four types, as well as its absorption rate in the body is the highest.
Although it cannot be directly utilized by the human body, it has the same effect and function with adenosylcobalamin.
2. Hydroxocobalamin
It is dark red crystals or crystalline powder with better solubility in water. Sometimes it is called long-acting cobalamin due to its slow metabolism in the urine. Compared with cyanocobalamin and methylcobalamin, hydroxocobalamin can reach a higher concentration in the eye, which is beneficial to relieve visual fatigue and be nutritional to the optic nerve, so resulting in a certain effect on toxic amblyopia from tobacco.
In addition, hydroxocobalamin can rapidly combine with free cyanide in aqueous solution to form non-toxic cyanocobalamin, and it has been approved by many countries for the treatment of known or suspected cyanide poisoning.
3. Methylcobalamin
It is a bright red needle crystal or crystalline powder. Its absorption rate in the human body is second to cyanocobalamin. In comparison with the other three types, it has a better transmission of nerve tissue, which can promote the metabolism of nucleic acid-protein-lipid and can repair damaged nerve tissue.
Clinically, it has obvious curative effect on peripheral nerve diseases such as neurological disorders, multiple neuritis caused by diabetes, especially numbness, pain, and paralysis. In the treatment of peripheral neuropathy, the clinical safety and efficacy of mecobalamin are superior to adenosylcobalamin and cyanocobalamin.
4. Adenosylcobalamin
It is a yellow-orange hexagonal crystal that becomes deep red when exposed to air. Adenosylcobalamin is used internationally as a biochemical reagent and test reagent.
At present, only the Chinese Pharmacopoeia takes it as a drug. Adenosylcobalamin has been used in the Chinese market for many years and its role is basically the same as that of the other three types. It is used not only for the treatment of megaloblastic anemia, but also for malnutrition anemia, anemia during pregnancy, and leukopenia caused by radiation and chemotherapy drugs.
Adenosine cobalamin can increase hemoglobin content and improve anemia in the body.
Here let’s introduce Cyanocobalamin more.
Property
Appearance
Crimson crystals or crystalline powder with flavorless and tasteless.
Stability
The stability is not good and decomposed when exposed to light so the storage condition should be protected from light. Also, it is easy to absorb moisture in the air.
Solubility
Slightly soluble in water or ethanol. Soluble in alcohol, insoluble in acetone chloroform and ether.
Molar mass
1355.38 g/mol
Chemical Formula
C63H88CoN14O14P
Chemical Structure
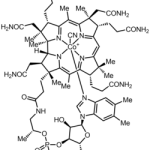
What Are Food & Feed Uses Of Cyanocobalamin?
Food
It is widely used as a supplement in cereal products and certain beverages. ‘Dietetic’ foods such as slimming foods and infant formulas are often fortified with vitamins, including B12. Fortification with Vitamin B12 is especially important for products aimed at people with a low dietary intake, such as vegans.
Feed Additives/Poultry
It is an indispensable micronutrient for the growth of the animals. Feed grade cyanocobalamin can promote the growth and development of poultry, especially young poultry.
The lack of Vitamin B12 in non-ruminant animals such as pigs and chickens will result in the stagnation of growth and development, and a few pigs may develop mild normal red cell anemia. In addition, the hatching rate of chickens and the reproductive rate of pigs can also be reduced with the deficiency of vitamin B12. The clinical symptoms of deficiency include loss of appetite, stagnation, anemia, and severe neurological symptoms.
What Are Possible Side effects?
It is generally considered safe but possible side effects of cyanocobalamin injection include allergic reactions such as hives, difficult breathing; redness of the face; swelling of the arms, hands, feet, ankles or lower legs; extreme thirst; and diarrhea. Less-serious side effects may include headache, dizziness, leg pain, itching, or rash.
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cyanocobalamin
Two FAQs
1. Does Cyanocobalamin Contain Cyanide?
Yes, Cyanocobalamin contains cyanide, but Don’t be panic as the percentage is very little and will be excreted from the body. Our body can deal with small amounts of cyanide, usually by using sodium thiosulfate, converting the cyanide ions to thiocyanate, which will be excreted from body. Cyanocobalamin is safe and used as food additives and can be found in many health supplements.
According to the European Food Safety Authority, “Data of from a Norwegian dietary survey show that the average and high (97.5th percentile) daily intake of [cyanide] among consumers amounts to respectively 95 and 372 micrograms/person or 1.4 and 5.4 micrograms/kg bw/day.” The amount of cyanide in a 1,000 microgram cyanocobalamin is 20 micrograms. (1)
Nature Sources Of Cyanide
The safety of cyanocobalamin has raised health concerns due to cyanide. Cyanide is widely found in nature. Cassava, sorghum, corn, beans, millet, cabbage, flaxseed, bamboo, and other plants contain cyanide. Cyanide in edible plants is mostly in the form of cyanide glycosides.
There are at least more than 2,000 species of plants that contain this component, of which about 1,000 are core species. People usually eat almonds, bayberry, grape seeds, apple seeds, peaches, plums, and cherries, and their cores contain cyanide.
In addition, small amounts of hydrogen cyanide are also detected in milk, distilled spirits, and fruit and wine products sold on the market; trace amounts of cyanide are also detected in some grains and water.
2. What Is The Difference Between Methylcobalamin And Cyanocobalamin?
They’re two forms of Vitamin B12. Cyano group at the cobalt is replaced with a methyl group that makes the difference between methylcobalamin and cyanocobalamin.
Cyanocobalamin and methylcobalamin are the same compounds with only one molecule differentiating the two. Cyanocobalamin has a cyanide donor, meaning that a molecule of cyanide is attached to the cobalamin compound. Instead of cyanide, methylcobalamin has a methyl donor attached to the cobalamin compound. Though the difference is small, it can have an impact on your health.
Specification
Feed Grade
Carrier: Corn starch, Calcium Carbonate
Character: Pale red powder, easy to absorb moisture
- Promote the generation of livestock and poultry
- Prevent pellagra, infectious dermatitis, poor fledging so that promote the growth.
- Increase the rate of incubation and at the same time decrease the rate of dead embryos.



