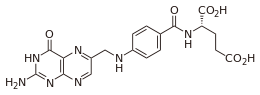
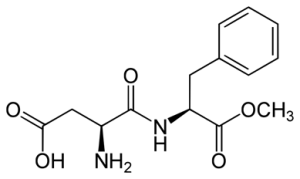
What is Pectin?
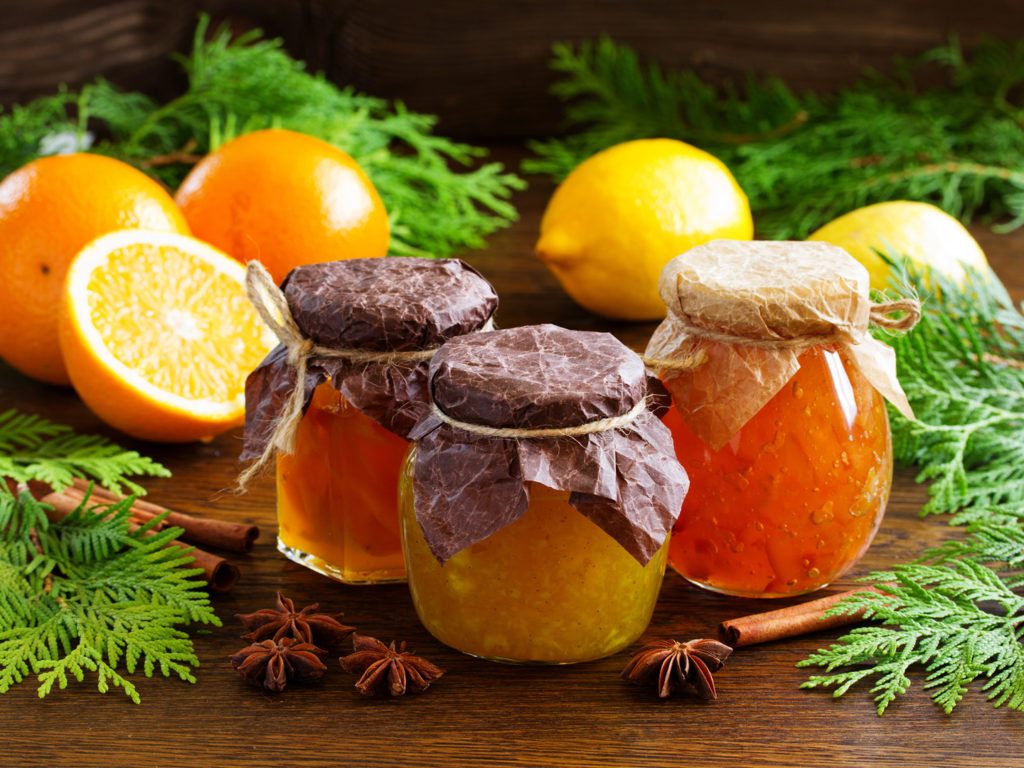
Pectin is used as a gelling agent, thickener, stabilizer in jams, jellies, dessert fillings, fruit juices and milk drinks and other food products. In europe, it is approved as a food additive with the E number E440.
It is manufactured by aqueous extraction of the appropriate edible plant materials, mainly from the citrus peel or apple pomace, followed by selective precipitation using alcohol or salts. The major fruits source used for the production of industrial pectin products usually come from apple and citrus peel.
Definition
Pectin is defined as a polymer containing galacturonic acid units (at least 65%). The acid groups commonly combine with methanol as a methyl ester or combine with sodium, potassium, calcium or ammonium as salts, and amide groups may also be present in some pectins.
Natural Sources
Pectin can be found in the fruits, roots, stems, and leaves of plants in the form of protopectin, pectin and pectic acid. It is a natural component located in the plant cell walls, presents along with cellulose and constitutes an adjoining layer in the middle of the cell, allowing the cells of the plant tissue to bind tightly together.
It is a linear polysaccharide polymer containing from several hundred to about 1000 anhydrogalluronic acid residues with a corresponding average relative molecular weight of 50,000 to 150,000. It is a soluble dietary fiber, part of galluronic acids are present as the methyl ester.
Pectin amount in fruits varies from the type of fruit. The following are the fruits with high, average and low pectin contents.
- High: lime, lemon, orange, and apple
- Average: apricot and blackberry
- Low: cherry, peach, and pineapple
Three Types Of Pectin
There are three types of pectin according to degree of methoxylation (DE) the in the market: high methoxyl pectin, low methoxyl pectin and amidated low methoxyl pectin.
It can also be divided into the rapid set and slow set pectin depending on the various operations.
High Methoxyl Pectin
The ratio of esterified to non-esterified galacturonic acid determines the behavior of pectin in food applications. More than 50% galacturonic acid are combined with methanol named as High methyl ester pectin or HM pectin.
Structure
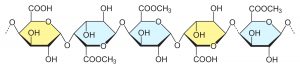
It is produced by the normal extraction process contains more than 50% of methoxyl groups and is classified as high methoxyl (HM) pectin. HM Pectin forms gels in aqueous systems with high contents of soluble solids (higher than 65%) and low pH values 2.0 – 3.8.
It can be used in high sugar jams, jellies, and beverages. HM pectin can be divided into a rapid set, medium rapid set and slow set pectin depending on the setting time and temperature.
Gels made with HM pectins have a firm and short structure, and are clear, with a good flavor release. These gels are not heated reversible.
Lower Methoxyl Pectin
less than 50% galacturonic acid are combined with methanol named as Low methyl ester Pectin or LM Pectin.
Structure
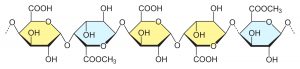
LM pectin forms gels in the presence of polyvalent cations, typically calcium (minimum quantity of 15 mg Ca++ / g pectin). LM pectin forms gel over a wide range of pH, from 2.6 to 7.0, and with a soluble solid content between 10 – 70%.
The higher the solids level and the lower the pH, the pectin is more reactive. The higher the calcium content and lower the pH, the higher the setting temperature. Low methoxyl Pectin can be used in organic jams and bakery jams.
Amidated Low Methoxyl Pectin
Amidated pectin (LMA) is a low methoxyl pectin obtained from high methoxyl pectin when ammonia is used in the alkaline de-esterification process. The degree of methoxylation (DE) and the degree of amidation (DA) determine the calcium reactivity of this pectin. LMA pectin form spreadable, shear reversible gels in hot and cold conditions.
LMA pectins are typically standardized according to the gel strength, setting temperature and calcium reactivity. It can be used in low sugar jams, fruit preparations and reversible jellies in hot and cold conditions.
Property
Appearance
A light yellowish powder with no smell. It solubles in 20 times the water and forms a viscous liquid.
Solubility
Pectin must be completely dissolved to ensure full utilization and to avoid heterogeneous gel formation. Any lumps formed during the preparation of the solution leads to loss of gel strength because the lumps are not active.
It is recommended to pre-blend pectin with sugar in the minimum ratio of 1:3 and dissolved preferably in hot water (85 – 90°C), at a soluble solids content below 20% using a suitable high-speed stirrer. Pectin will not dissolve in media where gelling conditions exist.
Storage Stability
Pectin should be stored in a cool dry environment. At increased temperatures, above ambient, the degradation of pectin will occur due to the reduction of molecular weight. The optimal pH for pectin is between 2.8 and 4.7.
Viscosity
Pectin solutions show lower viscosity compared to other thickening agents. Polyvalent salts (such as Ca++ and Mg++) increase the viscosity of LM pectin solutions. In calcium-free solution, the viscosity drops when the acidity is increased.
Gelation Mechanism
Different types of pectin with various behavior of gelation.
The optimal conditions for gelation of the different types of pectin are shown in the table below.
| Parameters | HM pectin | LM pectin |
| Degree of methoxylation (DM) | > 50% | < 50% |
| Soluble solid content (%) | ≥ 65% | 10 – 70% |
| pH | 2.0 – 3.8 | 2.6 – 7.0 |
| Bivalent ions, Ca++ (mg/g) | – | ≥ 15 |
What Are Uses In Food?
Pectin can be used for its gelling, thickening and stabilizing properties in food products. We can commonly find pectin in the label of jams and fruit jellies.
Let’s see the applications and functions:
Jam & Jelly
It can make the finished product delicate; full of elasticity and toughness; increase the aroma; make the mouthfeel smooth and refreshing. The recommended amount in jam & jelly: 0.3%-0.6%.
Ice Cream
It stabilizes the emulsion and makes the finished ice cream taste delicate and smooth. The Recommended uses level in ice cream: 0.1%-0.2%.
Yogurt, Lactobacillus, Fruit Juice & Drink
It acts as a stabilizer and thickener, which can prolong the shelf life of products, has a natural fruit flavor, the recommended uses level in yogurt: 0.1% -0.3%.
Baked Foods
It improves the permeability of the dough, enhances the taste and extends the shelf life. 0.3%-0.8% of the flour in baked foods.
What Are Possible Side Effects?
Allergy
It is generally recognized as safe, some people may be allergic to it and several symptoms may occur, such as stomach cramps, diarrhea, gas, and loose stools.