Sodium Saccharin E954
Sodium Saccharin is the first generation artificial sweetener, it is used widely in toothpaste than in food. This article share more information for this sweetener.
Saccharin and Sodium Saccharin E954
Saccharin
Saccharin is not the same with Sodium Saccharin. Another name of it is insoluble Saccharin, it is mainly used to produce Sodium Saccharin. The chemical formula as follows:
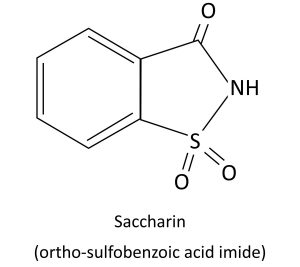
Chemical Name: O-Benzoic Sulfimide
Molecular formula:C7H5N03S
Molecular Weight: 183.19
Sodium Saccharin E954
E954 is the sodium salt of Saccharin. It is the first generation of artificial sweetener, its sweet degree is about 500 times than that of sugar. It is widely used in toothpaste, mouth wave, drinks, medicines, feed, electricity plating and etc. It’s harmless to the human body and it’s can not be absorbed by the body as it can be discharged completely through body metabolism.
It has two Specifications in the market, Dehydrate (with 15% water, CAS number 6155-57-3) and Anhydrous(with 6% water, CAS number 128-44-9).
Dehydrate
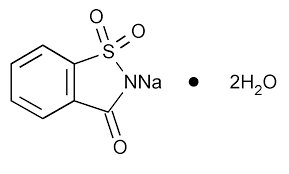
Dehydrate is with 15% water. It has 4-6 mesh,5-8 mesh,6-10mesh, 8-12mesh,8-16mesh,10-20mesh,20-40 mesh and 40-80 mesh in the market.
Chemical Name: Sodium O-Benzoic Sulfimide
Molecular formula: C7H4N03SNa2H20
Molecular Weight: 241.20
CAS number 6155-57-3
Anhydrous
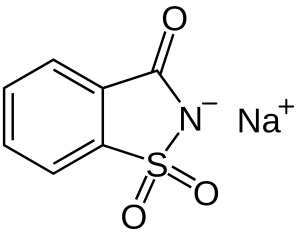
Another name of Anhydrous is Spray-dried with 6% water. It has 100mesh in the market.
Chemical Name: Sodium O-Benzoic Sulfimide
Molecular formula:C7H4N03SNa
Molecular Weight: 205.17
CAS number 128-44-9
Application & Use
In low-calorie and sugar-free food & beverage
Research also has shown that health professionals believe it is especially beneficial to obese individuals and persons with diabetes. Additionally, research indicates that E954 may help to reduce the risk of dental caries. It continues to be important for a wide range of low-calorie and sugar-free food & beverage applications.
It is used in such products as soft drinks, tabletop sweeteners, baked goods, jams, chewing gum, canned fruit, candy, dessert toppings, and salad dressings. Additionally, personal care products such as toothpaste, mouthwash, hygiene/cosmetic products, vitamins, and pharmaceuticals contain E954.
Sweeteners blends
The current availability of E954 and other low-calorie sweeteners, such as aspartame, acesulfame potassium, neotame, and sucralose, allows manufacturers to utilize a “multiple sweetener approach” — using the most appropriate sweetener, or combination of sweeteners, for a given product. Blending a variety of low-calorie sweeteners provides products with increased stability, improved taste, lower production costs, and more choices for the consumer.
Additionally, blending E954 with one or more low calorie sweeteners can result in sweetness synergy (the resulting sweetness is greater than the sum of the sweetness of the individual sweeteners), which can decrease the total amount of sweetener.
Sodium Saccharin E954 is stable when heated, even in the presence of acids, does not react chemically with other food ingredients, and stores well. In its acidic form, Saccharin is not particularly water-soluble. The form used as an artificial sweetener is usually its sodium salt. People restricting their dietary sodium intake sometimes use calcium salt, Calcium Saccharin.
In toothpaste?
It is a sugar substitute for toothpaste, mouthwash, beverages, table-top sweeteners, confectionery, electro-plating and etc. From our observing, there is lot of toothpaste that contains E954. The use quantity in toothpaste is more than 50% of its total consumption in the market.
It does not promote tooth decay in toothpaste while sugar can. Toothpaste must have thickeners to stay on the toothbrush and squeeze out of the tube. It must have detergents to remove fatty films, and water softeners to make the detergents work better, and sweeteners, preferably non-nutritive, so bacteria are not encouraged.
In the feed?
It is intended to be used as a sweetener in feed and water for drinking for piglets, pigs for fattening and veal calves. The Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed(FEEDAP) considers the proposed maximum use level of 150 mg/kg feed as safe for calves and pigs for fattening.
For piglets (sucking and weaned piglets), a lower level of 100 mg/kg complete feed is considered safe. The corresponding maximum safe concentrations in water for drinking are 30 mg/L for piglets and 50 mg/L for pigs for fattening, respectively.
Source: Safety and efficacy of sodium saccharin when used as a feed flavor for piglets, pigs for fattening, calves for rearing and calves for fattening
Benefits
Zero glycemic index and beneficial to diabetes
It may be useful for people with diabetes. Saccharin produces no glycemic response and may help control caloric intake. E954 is both calorie and carbohydrate free. It is appropriate to use it for medical and nutrition therapy (MNT) for people with diabetes, and dietetic professionals may incorporate saccharin into the individualized meal plans of their patients who have diabetes.
Zero calories
Meanwhile, it produces zero calories and is useful for people trying to control their weight. It may assist in weight management, control of blood glucose and prevention of dental caries. Replacing full-calorie products with it may help promote modest weight loss and may facilitate long-term maintenance of weight loss.
It has a long history (more than 100 years) of safe use and contributes no calories to the diet because the human body cannot metabolize it. (It is excreted in the same form it is ingested.)
Tooth health
Does not contribute to tooth decay. It is also inexpensive when compared with the second generation artificial sweeteners (aspartame and acesulfame k) and the third generation artificial sweeteners (sucralose).
Heat Stable
It is 500 times sweeter than sucrose. It has the ability to synergize the sweetening power of both nutritive and nonnutritive sweeteners, and its sweetening power is stable with heating. These factors make it an excellent food additive in manufactured products. During such blending of sweeteners, it can provide stability to maintain the product’s sweetness over a prolonged period of time. It also has a long shelf life.
As a tabletop sweetener, E954 is available in granular form (mostly 20-40 mesh and 40-80 mesh).
It is useful for consumers who want to create lower-calorie, lower-sugar versions of their favorite recipes. Because it is heat stable it is a good choice for use in cooking, baking, and canning/preserving. Depending on the type of recipe, e951 may be used to replace 50-100 percent of the sugar without sacrificing taste or other aspects of palatability.
Safety
It has been the subject of extensive scientific research. It is one of the most studied ingredients in the food supply. Although the totality of the available research indicates it is safe for human consumption, there has been controversy over its safety.
The basis for the controversy rests primarily on findings of bladder tumors in some male rats fed with high doses. Considerable research, however, indicates safety at human levels of consumption.
In addition, the level of human consumption of is very small compared to the levels used in rat studies. Further, although past research found an increased risk of bladder tumors in male rats ingesting with high amounts, additional research has discovered that the mechanism by which the tumors developed was specific to male rats and does not apply in humans.
The average user ingests less than one ounce of the sweetener each year. The following scientific data demonstrates its safety:
Extensive research on human populations has established no association between sodium saccharin and cancer. More than 30 human studies indicated it is safety at human levels of consumption. These studies include multiple generations of users.
In 14 single-generation animal studies involving several species of animals, it did not induce cancer in any organ, even at exceptionally high dose levels.
The body does not metabolize it and does not react with DNA (nucleic acid present in all living cells).
E954 is approved in more than 100 countries around the world and has been determined to be safe by regulatory agencies around the world, including the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), Health Canada, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and the Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) of the World Health Organization (WHO).
In summary, research conducted over the past 25 years and a history of human use of over 100 years overwhelmingly demonstrate that it does not cause cancer in humans.
Safety supported
1993 – World Health Organization (WHO) Confirmed as a safe artificial sweetener for human consumption
1998 – International Agency for Research on cancer (iARc) Deleted from list of carcinogen
2000 – National Toxicology Program (nTP) Deleted from list of carcinogens
2001 – Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Declared safe for human consumption
2010 – Environmental Protection Agency (ePA) Deleted from list of toxic materials
2011 – The Wall street Journal (WsJ) Us President Barack Obama commented that the ePA’s decision to eliminate the regulation on saccharin was wise.
Side Effects
Discovered in 1879 and 500 times sweeter than table sugar, It is added to some foods to reduce the calorie count without stripping the food of its sweet flavor. Though there is some controversy about the use of artificial sweeteners and health, it is recognized as safe by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Certain diet and low-calorie foods contain saccharin, and they include the artificial sweetener in the ingredient list.
It is approved for use in food as a non-nutritive sweetener. It is 500times sweeter than table sugar (sucrose), and it does not contain any calories.
First discovered and used in 1879, sodium saccharin is currently approved for use, under certain conditions, in beverages, fruit juice drinks, and bases or mixes when prepared for consumption in accordance with directions, as a sugar substitute for cooking or table use, and in processed foods. It is also approved for use for certain technological purposes.
In the early 1970s, it was linked with the development of bladder cancer in laboratory rats, which led Congress to mandate additional studies and the presence of a warning label on saccharin-containing products until such warning could be shown to be unnecessary. Since then, more than 30 human studies demonstrated that the results found in rats were not relevant to humans, and that it is safe for human consumption.
In 2000, the National Toxicology Program of the National Institutes of Health concluded that it should be removed from the list of potential carcinogens. Products containing saccharin no longer have to carry the warning label.
Source: Additional Information about High-Intensity Sweeteners Permitted for Use in Food in the United States.
Sodium Saccharin VS Aspartame
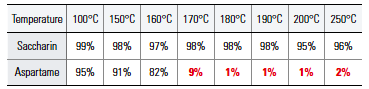
Its strength over aspartame is not only limited to its economic value. It can also be preserved for a long period of time without decomposition and can also act as an effective stabilizer. Moreover, it is thermal resistant. In an experiment, E954 and Aspartame E951 were heated for 30 minutes.
In the final results, E954 did not show any change in its composition, regardless of temperature. On the other hand, aspartame started to decompose at 150°C, became 91% decomposed at 170°C, and decomposed completely after 180°C. The final results appear that aspartame is not appropriate as a sweetener for high temperature usage in food such as baked goods.
Thermal resistance Comparison Between E954 and E951
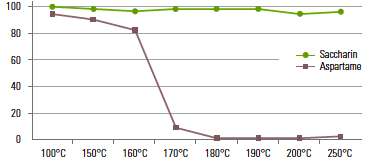
Decomposition Rate According to Temperature
Market Trend
Sodium Saccharin is one of the oldest artificial, non-nutritive sweeteners. It has no caloric value and our body does not metabolize it and excrete unchanged. It is also better for oral health (such as toothpaste, mouth wave) as compared to table sugar since it does not promote tooth decay.
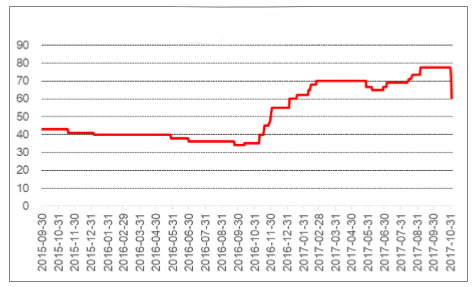
We can easily find it in the food and beverage industry in diet carbonated drinks and other low-calorie products. According to the latest report by IMARC Group, titled “Saccharin Market: Global Industry Trends, Share, Size, Growth, Opportunity and Forecast 2018-2023”, the global saccharin market reached a value of US$ 260 Million in 2017. The market is further expected to reach a value of US$ 339 Million by 2023, growing at a CAGR of 6% during 2018-2023.
The rising health consciousness among the consumers regarding the negative effects of sugar consumption has led to an increase in the demand for artificial sweeteners. Since it is cheaper as compared to most other artificial sweeteners (aspartame, acesulfame k, sucralose), it is used extensively in its end-use sectors. The use is also important for people who require a diet with the restriction on caloric or carbohydrate intake, such as diabetics.
Source: Saccharin Market: Global Industry Trends, Share, Size, Growth, Opportunity and Forecast 2018-2023
With the popularity of plant-based sweeteners and other artificial sweeteners, we think the use may decrease especially in food and drink application, can the market keep go up? It’s hard to say.
Manufacturers
The capacity from China manufacturers takes a large number of global sodium saccharin market share, the manufacturers like Keifeng, Tianjin North Food (TNF), Changjie and Shanghai Fortune who are in the market for years, China manufacturers export Dehydrate (with 15% water, CAS number 6155-57-3) 20-40mesh and 40-80mesh much, other mesh sizes like 4-6 mesh,5-8 mesh,6-10mesh, 8-12mesh,8-16mesh,10-20mesh are little; also with Anhydrous(with 6% water, CAS number 128-44-9). There is also a manufacturer in Korea, named JMC.
Shanghai Fortune won the antidumping case for USA market so it had more advantages than other China manufacturers. Shanghai Fortune together with JMC take over more than 80% market share in USA during the antidumping.
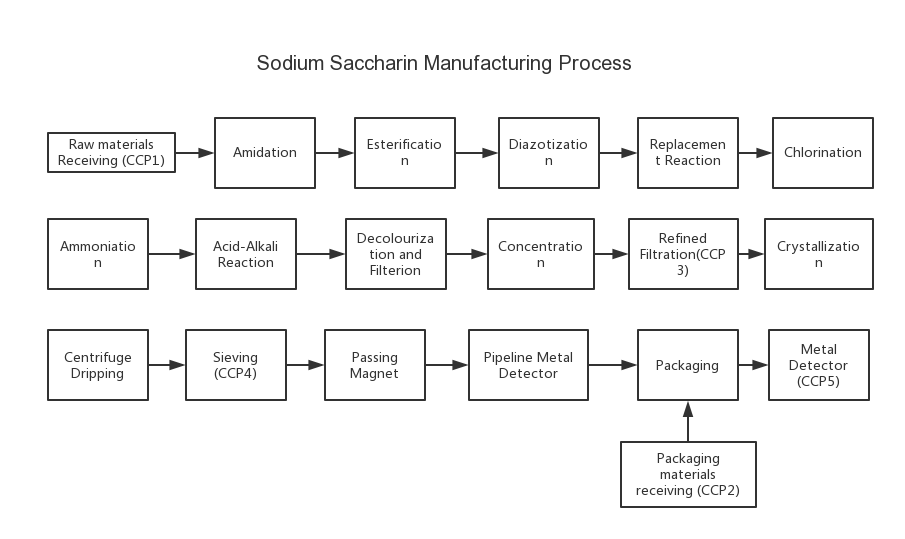
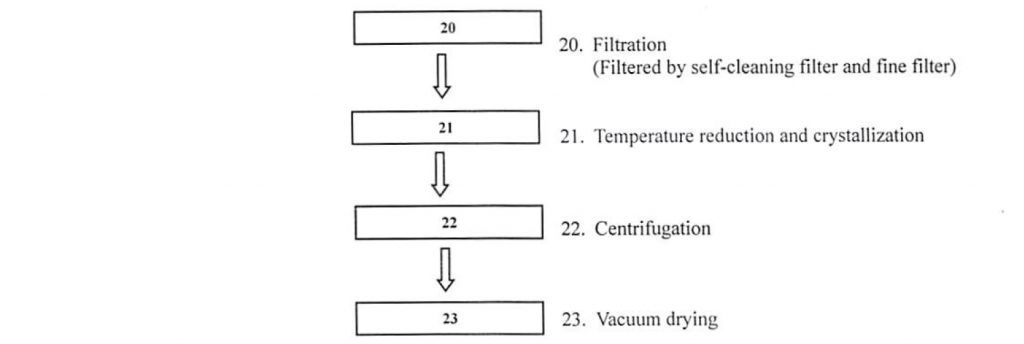
Manufacturing process
The manufacturing process is from chemical synthesis. The raw materials used as follows: Phthalic Anhydride, Ammoonia, Sodium Hydroxide, Methyl Alcohol, Sodium Hydroxide, Hydrochloric Acid, Sodium Nitrite, Copper Sulphate, Sulphur Dioxide, Toluene, Liquid Chlorine, Ammonia, Sodium Bicarbonate, Potassium Permanganate, Sodium Pyrosulfite.


 What is Vitamin B1 Thiamine Hydrochloride?
What is Vitamin B1 Thiamine Hydrochloride?