What is Folic Acid?
Folic acid is a form of folate (a B vitamin, Folic Acid is chemical synthesized while Folate is from natural food) that both human beings and animals need. It is water soluble and also called Vitamin B9. Folic acid is important for pregnant it protects unborn babies against serious birth defects. Folic acid powder is used multi-vitamins products and fortified foods, such as breads, pastas and cereals, beverages, soft drinks and baby foods.
Property
Vitamin B9 Folic Acid is a yellow or orange yellow crystalline powder, odorless and tasteless, insoluble in water, ethanol, acetone, chloroform and ether, but freely soluble in dilute solutions of alkali hydroxides or carbonates. Folic Acid is a member of the B vitamin family that widely used in feed, food and nutraceutical applications. The natural form Folate is found in many foods including dark leafy vegetables, fruits and animal.
Molecular Formula
C19H19N7O6
Chemical structure
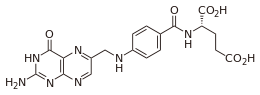
Molecular Weight
441.40
CAS No.
59-30-3
Another name for folic acid
5′-methyltetrahydrofolate, 5′-MTHF, Acide Folique, Acide Ptéroylglutamique, Acide Ptéroylmonoglutamique, Acido Folico, B Complex Vitamin, Complexe Vitaminique B, Dihydrofolate, Folacin, Folacine, Folate, Folinic Acid, L-methylfolate, Methylfolate, Pteroylglutamic Acid, Pteroylmonoglutamic Acid, Pteroylpolyglutamate, Tetrahydrofolate, Vitamin B9, Vitamine B9.
Is folic acid a B vitamin?
Yes, Folic Acid is a B vitamin and is often used in combination with other B vitamins in vitamin B complex formulations. Vitamin B complex generally includes vitamin B1 (Thiamine Hydrochloride and Thiamine Mononitrate), vitamin B2 (riboflavin), vitamin B3 (niacin/niacinamide), vitamin B5 (D-Calcium Pantothenate), vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine Hydrochloride), vitamin B7 (D-Biotin), vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) and Vitamin B9 (Folic acid).
Types of folic acid Vitamin B9
Depends on Folic acid Vitamin B9 is food grade or feed grade or pharmaceutical grade, commonly in the market the types of folic acid according to different folic acid content: 10%, 80% and pure as raw material. As a folic acid manufacturer and supplier, we sell the main types in the market:
- folic acid pure powder
- 80% folic acid powder
- 10% folic acid powder
Vitamin B9 Folic acid Synthesis/manufacturing process
Following Raw materials are used during Vitamin B9 Folic acid Synthesis/manufacturing process: three chloro acetone, sodium carbonate, three aminopyrimidine sulfate, caustic soda, p-Aminobenzoyl glutamic acid, sulfuric acid, activated carbon.
Why take Folic acid when pregnant and what does folic acid do during pregnancy?
Vitamin B9 Folic acid is a water-soluble B vitamin, and the demand for folic acid in pregnant women is 4 times higher than normal people. Why take Folic acid when pregnant is that the early pregnancy period is the critical period of placental formation, cell growth, cleavage and the differentiation of the fetal organ system. Folic acid deficiency in pregnancy can lead to fetal malformation. For example, in China, the incidence of neural tube defects is about 3.8, including anencephalon, spina bifida, and so on. It may also cause early spontaneous abortions.
By the second trimester, during the third trimester, in addition to fetal growth and development, maternal blood volume, breast and placental development have increased the need for folic acid. Folate deficiency, pregnant women prone to placental abruption, pregnancy-induced hypertension syndrome, megaloblastic anemia; fetal prone to intrauterine growth retardation, premature delivery and low birth weight, and such fetal growth and mental development after birth will be subject to influences.
Before preparing to conceive, expectant mothers and fathers should maintain a happy mood in addition to basic smoking cessation and alcohol abstinence. Women who are preparing to become pregnant should start taking 400 μg of folic acid daily before pregnancy. American researchers found that if women begin to take folic acid early in pregnancy, the risk of cleft lip in future infants can be reduced. In addition, it is important for expectant mothers to take vitamins correctly during pregnancy, compound vitamins (rich in vitamins A, B6, B12, C, folic acid) and minerals (1000 mg of calcium, 500 mg of magnesium) is also very important to prevent baby’s brain and nerve defects.
What does folic acid do in the body?
Vitamin B9 Folic acid d0 a lots work in our body and the role it mainly plays as follows:
- As a co-enzyme for the one-carbon unit transferase system in biochemical reactions, Folic acid plays as a one-carbon unit transferor.
- Participate in the synthesis of purine and thymine, and further synthesize DNA and RNA.
- Involved in amino acid metabolism, Folic acid function as a carrier for one carbon unit during the interconversion between glycine and serine, histidine and glutamic acid, homocysteine and methionine.
- Folic acid helps synthesis of hemoglobin and methyl compounds such as epinephrine, choline, creatine and the like.
- Folic acid plays an important role in the synthesis of proteins, nucleic acids and metabolism of various amino acids.
- Folic acid helps purine and pyrimidine synthesis: As a coenzyme involved in the synthesis of purines and pyrimidines in nucleic acid synthesis, it plays a role in cellular DNA synthesis.
- Folic acid helps amino acid transformation: Involvement in the conversion of two-carbon amino acids and three-carbon amino acids. It promotes the conversion of phenylalanine and tyrosine, histidine and glutamic acid, cysteine and methionine. In addition, folic acid is also a component containing iron hemoglobin.
Vitamin B9 Folic acid recommended daily intake
The recommended daily intake of folic acid in the US is 400 micrograms from foods or dietary supplements and the most over-the-counter supplements of folic acid are 400 mcg tablets. The U. S. Public Health Service and CDC recommend that all women of childbearing age consume 0.4 mg (400 micrograms) of folic acid daily to prevent two common and serious birth defects, spina bifida and anencephaly. 400 micrograms is the amount of folic acid during pregnancy.
Vitamin B9 Folic acid deficiency
Vitamin B9 Folic acid deficiency can lead to the block of forms of deoxythymidylate, purine nucleotides, and the interconversion of amino acids. And DNA synthesis will be reduced intracellular, and the disorder of cell division and maturation, causing megaloblastic anemia. Vitamin B12 deficiency and folic acid deficiency are basically similar, all can all cause megaloblastic anemia, white blood cell and thrombocytopenia, and gastrointestinal symptoms such as loss of appetite, abdominal distention, diarrhea, and glossitis, etc, with the most prominent glossitis, red tongue. The tongue papilla is atrophic and has a smooth surface, commonly known as “tongue tongue”, with pain.
Vitamin B12 deficiency is often accompanied by nervous system performance, such as fatigue, numbness of hands and feet, sensory disturbances, walking difficulties and other peripheral neuritis, subacute or chronic degeneration of spinal cord combined with the performance of the posterior lateral cord; Folic acid deficiency common in pernicious anemia, pediatric and elderly patients often appear Mental symptoms such as cravings, drowsiness, or confusion.
Vitamin B9 Folic acid deficiency can cause emotional changes, but the deficiency can disappear if take folic acid supplement. The deficiency of folic acid in pregnant women can increase the prevalence of preeclampsia and placental detachment. Pregnant women with megaloblastic anaemia are prone to intrauterine growth retardation, premature delivery and low birth weight. Deficiency of folic acid in early pregnancy can lead to fetal neural tube defects (such as spina bifida, anencephaly, etc.). Folic acid deficiency can also cause hyperhomocysteinemia, thereby increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease. Intestinal diseases can interfere with the absorption of folic acid in foods and the recycling process through the enterohepatic circulation, so folic acid deficiency is a common complication of small bowel disease.
Too much folic acid Vitamin B9
Vitamin B9 Folic acid is a water-soluble vitamin that is considered generally safe if intake not too much, for example, 20 times the adult minimum requirement. The excessed/too much Folic acid bound to polypeptide in serum and tissue will excreted in the urine. The toxic effects of taking large doses of folic acid may as follows:
- Interfering with the effects of anticonvulsant drugs induces convulsive seizures.
- Oral intake 350 mg of folic acid may affect the absorption of zinc, leading to zinc deficiency, retarding fetal development and increasing the number of low birth weight infants.
- Covering the early manifestations of vitamin B12 deficiency causes damage to the nervous system.
How is Folic acid metabolism in body?
After being absorbed in the intestine, Vitamin B9 folic acid enters the liver through the portal vein and is converted into active tetrahydrofolate by the action of intrahepatic dihydrofolate reductase. The latter is the carrier that transfers the “one carbon group” in the body and is the main factor in DNA synthesis. After orally intake, it is almost completely absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract (mainly in the upper part of the duodenum), appears in the blood 5-20 minutes later, and reaches the highest plasma concentration after 1 hour. Most of Folic acid is stored in the liver, and folic acid in the body is mainly decomposed into purine and p-aminobenzoyl glutamic acid.
The plasma half-life is about 40 minutes. Folic acid discharged from the bile to the intestine can be absorbed again, forming a hepatic intestine circulation. In chronic alcoholism, the daily intake of folic acid (Folate) from food is greatly limited, and the enterohepatic circulation of folic acid may also be impaired by the toxic effects of alcohol on hepatic parenchymal cells.
Vitamin B9 Folic acid Function
Vitamin B9 Folic acid is involved in many functions but especially in the formation of red blood cells and in the normal development of the neural tube – the structure that becomes the brain and spinal cord in the foetus. Folic acid main functions as follows:
- Help body use amino acids, the building blocks of proteins
- Help body produce nucleic acids (like DNA), the body’s genetic material
- Form blood cells in the bone marrow to
- Ensure rapid cell growth in infancy, adolescence, and pregnancy
- Control (together with vitamin B6 and vitamin B12) blood levels of the amino acid homocysteine, associated with certain chronic conditions like heart disease.
Vitamin B9 Folic acid Benefit
Vitamin B9 Folic acid benefits not pregnant
Vitamin B9 Folic acid is a kind of B vitamin. It slightly soluble in water, unstable to heat, light and acidic solution, stable to heat in neutral and alkaline solution, and loss up to 50~90% during cooking. Folic acid can not only benefit pregnant but also have other benefits:
- Folic acid is a coenzyme help the synthesis of nucleic acids. The nucleic acid synthesis and normal cell division and replication will be affected if Folic acid deficiency.
- Folic acid helps regulate the development of embryonic neurons and prevents newborn infants from developing congenital neural tube defects.
- It (with Vitamin B12) is a must for the production of red blood cells and prevent the treatment of folate anemia.
- Protecting the mucous membranes and mucous membranes is a very active part of cell division, decline, and regeneration.
- Folic acid helps anti-cancer effect, and together with niacin can prevent free radicals from damaging the chromosomes.
Vitamin B9 Folic acid Side effects
Vitamin B9 Folic acid is LIKELY SAFE for most people when taken by mouth or injected into the body. Most adults do not experience any side effects when used in doses less than 1000 mcg daily.
Folic acid is POSSIBLY UNSAFE when taken by mouth in large doses, long-term. High doses of folic acid might cause abdominal cramps, diarrhea, rash, sleep disorders, irritability, confusion, nausea, stomach upset, behavior changes, skin reactions, seizures, gas, excitability, and other side effects.
Reference: https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-1017/folic-acid
Vitamin B9 Folic acid Use
In Food
Food grade Folic acid can be used in nutrition fortified foods such as Folic acid bread, folic acid milk, folic acid chewing gum, folic acid drink and folic acid flour, breakfast cereals and baby foods.
In feed
Vitamin B9 Folic acid consumption in feed takes a large part of total folic acid, around 75%. Feed grade folic acid can be used as feed additives and has a significant role in feed. Feed additives are raw materials that must be used in the modern feed industry. It has obvious effects on strengthening the nutritional value of the basic feed, improving animal production performance, ensuring animal health, saving feed costs, and improving livestock product quality. Folic acid is originally isolated from plants, so it is called folic acid and it is involved in the metabolism of substances in the animal’s body in the form of tetrahydrofolate. The transfer of a carbon group participates in the synthesis of pyrene, pyrimidine, and amino acid metabolism, thereby affecting the synthesis of nucleic acids and the metabolism of proteins, promoting the formation of normal blood cells, and promoting the production of immunoglobulins.
Vitamin B9 Folic acid deficiency in animals often causes anemia, decreasing of red blood cells, slow or stopped stopped. The symptoms like spinal palsy, feather decoloration, reduced reproductive capacity and high embryonic mortality will exist in birds. Particularly noticeable is the embryo’s temporal bones are short and staggered; pigs will have dermatitis and the symptoms of hair removal and the hurt digestive organs, respiratory organs and urinary mucosa.
Vitamin B9 Folic acid is one of the B vitamins, which can promote the maturation of young cells in bone marrow, promote growth and promote the formation of hematopoietic factors. Folic acid has the effect of promoting ovulation and increasing the number of follicles. Folic acid is added to the sow’s feed to increase the litter size. Folic acid is added to the feed of laying hens to increase the egg production rate.
Recommended dosage in feed
| Piglet | 0.6~0.7mg/kg |
Growth Fei Yuzhu |
0.3~0.6mg/kg |
| fish | 1.0~2.0mg/kg |
chick |
0.6~0.7mg/kg |
| Laying hens | 0.3~0.6mg/kg |
Laying hens |
0.3~0.6mg/kg |
| broilers | 0.6~0.7mg/kg | – | – |
In Pharmaceuticals and Healthy foods
In the pharmaceutical industry, folic acid is essential for the growth and reproduction of cells in the human body. It plays an important role in the metabolism of the human body and is one of the indispensable nutrients for the human body, especially for pregnant women, nursing mothers and infants who account for a large proportion of the population. Young children also need to supplement with folic acid. Folic acid is a significant drug for megaloblastic anemia. Therefore, there is a very broad market prospect for the development of folic acid pharmaceuticals and folic acid health foods.
What is Folate?
Folate and Folic acid are often used interchangeably but there are differences between them. Folate is the naturally-occurring form of the vitamin B9.
Food sources of Folate
Vegetables source
Good sources of folate from lettuce, spinach, asparagus, broccoli, rape, bok choy, greens, lentils, pods, tomatoes, carrots, squash, mushrooms, etc.
Fruits source
oranges, strawberries, cherries, bananas, lemons, peaches, plums, apricots, bayberry, jellyfish, wild jujube, hawthorn, pomegranate, grapes, kiwi, pears, walnuts, apples, etc. These are good sources of folate from fruits.
Animal foods source:
Folate rich foods in animal liver, kidney, poultry meat and eggs, such as liver, beef, lamb, chicken, egg yolk and so on.
Beans, Nuts source
Soybeans, soy products, walnuts (including walnut oil), cashews, chestnuts, almonds, pine nuts, etc.
Cereals source
Cereals foods high in folate whole wheat flour, barley, rice bran, wheat germ, brown rice and so on.
Is Folate better than Folic acid?
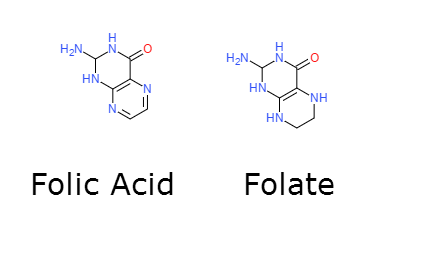
Folic aid is the synthetic form of the vitamin B9 that is used in most supplements and in fortified foods. (If your supplements lists “folate,” it suggests that food sources were used instead of synthetic folic acid.) The chemical structure of Folic acid is different with Folate.
Folic acid and folate work the same in the body, with one exception: Ironically, the synthetic form (folic acid) is better absorbed by the body than the natural form.
Interestingly, folic acid tends to be absorbed better than the folate found in food.
Many people think that natural Folate is better than Folic Acid as Folate is nature and more reliable than synthetic Folic acid. But if you look at the list of ingredients for the vitamin tablets you take every day, you’re more likely to see Folic Acid instead of Folate. This is because the Folic Acid absorption is more than twice that of Folate (natural folic acid). This does not mean that Folic Acid is better. The reason why manufacturers like to take Folic Acid to multivitamin supplements is that it can quickly relieve Folate deficiency and reduce the likelihood of congenital malformations in babies. And this is the reason pregnant choose to take Folic Acid to their diet during pregnancy.
Vitamin B9 Folic acid market
Market trend
It is expected that the application of Folic acid in health products and pharmaceutical products will drive the use of folic acid. Owing to the high medicinal value of folic acid, its consumption is expected to increase rapidly during the forecast period. Factors such as increasing health awareness and increasing awareness of the significance of folic acid for maintaining good health supports the growth of the folic acid market. Various health agencies also promote the use of folic acid in cereals products.
For example, the U.S. Department of Public Health and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend that all women of childbearing age take 0.4 mg (400 μg) of folic acid per day to prevent severe birth defects in children. The increasing purchasing power of consumers and their preference for nutritious and mineral-rich ready-to-eat foods may increase the demand for folic acid in the near future.
China is the big food and feed grade Folic acid manufacturers and export country in the world. China manufactures’ market takes around 90%.
Today’s price
Updated on 2018/05/26: Now the price for pure Folic acid powder is around RMB195/kg, the price in January was around RMB280/kg, it decreased around 30%.
Where to buy Vitamin B9 Folic acid?
You can buy food or feed grade Vitamin B9 Folic acid powder from us, Specification complies with BP/USP/EP/JP/FCC standard. As a Folic acid manufacturer and supplier, we sell food and feed grade Folic acid pure; 80% Folic acid and 10% Folic acid.
We’re committed to the quality and safety of our ingredients. We know that our customers expect us to use only the highest quality food additives & ingredients with better price, and we do everything we can to satisfy those expectations.
Usage: feed additives, food additives, pharmaceuticals and healthy foods
Storage
- It should be stored in a cool and dry place.
- Avoid the sun and rain should be in the process of transportation, heating and impact.
- Handling be careful not oxidizing and toxic or other polluting goods and material mixed, mixed transport.
Specification:
- folic acid pure powder
- 80% folic acid powder
- 10% folic acid powder
If you have any other questions, please email us through: info@foodsweeteners.com