What is Biotin (Vitamin B7)?
Biotin is a water-soluble B vitamin, also called vitamin B7 and formerly known as vitamin H or coenzyme R.
Biotin is essential for the synthesis of vitamin C and is an essential substance for normal metabolism of fats and proteins. Biotin can be found in all living cells. It is a nutrient to maintain the body’s natural growth, development and normal body functions.
Biotin is also required for the catabolism and utilization of the three branched-chain amino acids: leucine, isoleucine, and valine.
What’s the role of Biotin (Vitamin B7)
The human body needs about 100 to 300 mg D-Biotin per day. In raw egg white, there is an avidin protein (avidin) that binds with D-Biotin, and the combined D-Biotin cannot be absorbed by the digestive tract which will lead to the deficiency of D-Biotin in the animal body, that results in loss of appetite, glossitis, dermatitis, hair loss and so on.
However, the deficiency of D-Biotin have not yet be noticed in human beings, probably due to the fact that we intake foods high in Biotin or Biotin food sources; and intestinal bacteria can also synthesize D-Biotin. Biotin is a coenzyme of various enzymes in the human body, the role of Biotin involved in the metabolism of fatty acids and carbohydrates in the body; promoting the synthesis of proteins; also involved in the metabolism of vitamin B12, folic acid, pantothenic acid; and promoting urea synthesis and excretion.
Role of Biotin (Vitamin B7) and what it do?
- Fat metabolism: help fat, liver sugar and amino acids in the human body for normal synthesis and metabolism;
- Growth: promote the normal operation and growth of sweat glands, nerve tissue, bone marrow, male gonad, skin and hair, reduce eczema, dermatitis symptoms;
- Prevent: Biotin prevent white hair and hair loss, help to treat baldness;
- Ease muscle pain;
- Promote urea synthesis and excretion, purine synthesis and oleic acid biosynthesis.
- Treatment: help treatment of arteriosclerosis, stroke, lipid metabolism disorders, hypertension, coronary heart disease and blood circulation disorders.
Is Biotin (Vitamin B7) natural?
Biotin can be found in food, the type of Biotin is natural. Actually there are eight different forms of Biotin, but only one is naturally occurring — the kind found in food sources. This type is called “D-biotin” and is believed to be the only type that has full vitamin capabilities.
How many Types of Biotin (As raw material) in the market?
Depends on Biotin is food grade or feed grade or pharmaceutical grade, commonly in the market the types of Biotin are: 1%, 2%, 10% and pure as raw material. As a D-Biotin manufacturer and supplier, we sell the main types in the market:
- D-biotin pure;
- 10% D-Biotin food grade (Maltodextrin as carrier);
- 2% D-Biotin feed grade (Maltodextrin as carrier)
- 1% D-Biotin feed grade (Dicalcium Phosphate as carrier)
How is Biotin (Vitamin B7) absorption in body?
By oral intake, Biotin is quickly absorbed from the stomach and intestine. 80% of the Biotin in the blood is present in free form. It is distributed throughout tissues of the body and the content will be more in the liver and kidneys. It is excreted through the urine and only a little quantity is metabolized to Biotin oxides and double-lowering biotin.
What is (Vitamin B7) Biotin deficiency?
Biotin deficiency means the low biotin intake, and the deficiency symptoms would be as follows:
- increase the risk of dandruff, easy hair loss, juvenile white hair;
- dull complexion, blush, dermatitis;
- depression, insomnia, easy to sleep and other neurological symptoms;
- fatigue, lazy weakness, muscle pain.
Signs of biotin deficiency: including dermatitis, eczema, atrophic glossitis, hyperesthesia, muscle pain, burnout, anorexia and mild anemia, hair loss
What is D-Biotin (Vitamin B7)
There are eight different forms of Biotin, but only D-Biotin is naturally occurring found in food sources. D-biotin is believed to be the only type that has full vitamin capabilities. The form of Biotin that your body can use is D-biotin.
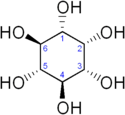
The D, refers to chirality. Two molecules that are chiral isomers of each other will have the same chemical formula and structure; the only difference is the arrangement of groups around certain carbon atoms. It’s often easiest to think of chirality as “handedness”, so your left and right hands are chiral isomers of each other. Same structure, mirror images. Chirality does cause some difference in function.
Whenever you see “Biotin” in the supplement label or website or other place, it’s commonly means D-biotin. And the Biotin we talk in this article is D-Biotin which has full vitamin capabilities.
It is a B Vitamin, other B vitamins are Vitamin B1 (Thiamine Hcl), Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin), Vitamin B3 (Niacin, Niacinamide), Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic acid), Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine Hydrochloride), Vitamin B9 (Folic acid) and Vitamin B12 (Cyanocobalamin).
D-Biotin (Vitamin B7) Properties
Appearance and Solubility
D-Biotin is a white or almost white, crystal powder or colorless crystal, very slightly soluble in water and ethanol, practically insoluble in acetone. It can be dissolved in a dilute solution of alkaline hydroxide. Solubility in water: 22mg/100ml
Other Name
Biotin, vitamin H ,vitamin B7
CAS NO
58-85-5
MOLECULAR FORMULA
C10H16N2O3S
Chemical Formula
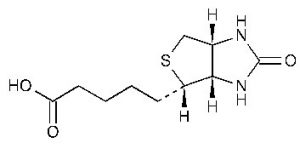
Where does (Vitamin B7) D-Biotin come from?
D-Biotin comes both from nature and chemical synthesis. Natural D-Biotin comes from food.
Food has biotin as follows
- Beef or pork liver
- Egg, cooked
- Yeast
- Whole wheat bread:
- Avocado
- Salmon
- Cauliflower
- Cheese
- Etc
How is pure D-biotin (Vitamin B7) made in chemical synthesis?
Pure D-Biotin manufacturing process
Pure D-Biotin made by chemical synthesis and the manufacturing process as follows:
Naphthenic acid – Dehydration – Reduction – Sulfurization – Grignard Reaction – Hydrogenation – Debenzylation – Refining – D-biotin
1% 2% D-Biotin feed grade manufacturing process
Pure D-Biotin – Dissolution – Spray drying – Mixing – Sieving – D-Biotin 2% SD
Dissolve pure Biotin, Sodium carbonate and Carbohydrate in water. The solution is transferred into the spray drying chamber and a flow aid is added in order to achieve appropriate flowability. Feed grade D-Biotin 2% is then obtained after sieving.
Vitamin B7 D-Biotin Use
In Food
D-Biotin can be used in many dietary supplements, infant milk formulas and baby foods – as well as various dietetic products. D-Biotin is often used in combinations of the B vitamins. It can be used for human nutrition fortification, used for solid preparation, suitable for dry infusion with water.
What is biotin used for in the body?
Why do people take D-Biotin? Biotin can be used for promoting the synthesis of certain proteins by helping the production of energy; at the same time, it can help cells grow, produce fatty acids, metabolize carbohydrates, fats and proteins, and help the use of vitamin B; promoting sweat glands, nerve tissue, The health of bone marrow and male gonads maintains the normal operation and growth of skin and hair, relieves eczema and dermatitis symptoms, prevents white hair and hair loss, helps to treat baldness, eases muscle pain, and definitely helps melancholia and insomnia. Participate in the metabolism of vitamin B12, folic acid, pantothenic acid; promote urea synthesis and excretion; improve the body’s immune function.
In Cosmetics
D-Biotin market for cosmetics is developing and the beauty and cosmetics industry is one of the major international industries. As a D-Biotin manufacturer and supplier, our customers are mainly in the field of cosmetics and feed.
D-Biotin has an excellent cosmetic effect, it can keep skin white and nails smooth. The total international sales of cosmetics and cosmetics related products are much higher than the sales of pharmaceuticals. New applications of biotin in the skin, nails and hairdressing will inevitably lead to pharmaceutical-grade organisms.
D-Biotin as a nutritional supplement, can be used as a B Vitamin in the food industry. It has the function of preventing skin diseases and promoting lipid metabolism in cosmetics use.
It can increase the blood circulation speed in skin blood vessels. It is easy to mix the oil phase in the formula with concentration range from 0.1% to 1.0%. It can be used in skin creams, sports liquids, foot antiperspirants, shave lotions and shampoos in cosmetics use.
In Feed
D-Biotin is one of the B vitamins necessary to maintain normal physiological functions in the animal’s body. D- Biotin can be widely seen in feed additives plus animal intestines can synthesize D-Biotin, it was previously thought that it’s okay if animals feed do not add D-Biotin. However, D-Biotin deficiency often occurs especially under intensive production conditions, and D-biotin deficiency symptoms are more likely to occur.
The deficiency of D-biotin in livestock and poultry results in slow growth, reduced feeding, decreased breeding performance of female animals, and meat quality as well. Carcass week, dermatitis, and even death will also happen. The intake of D-biotin can improve the above symptoms. As a result, people re-emphasize and study the nutritional effects of D-biotin and its mechanisms. In recent years, D-biotin has become one of the most popular water-soluble B vitamins.
D-Biotin Properties
d-Biotin can be found in plants and animals, and naturally occurring D-biotin exists mainly in combination with other molecules. Its chemical structure includes a carboxyl side chain containing five carbon atoms and two five-membered heterocycles, which binds to the ε-lysine residue of the enzyme protein in the body and acts as a coenzyme. Biotin may have 8 different isomers, of which only D-biotin has biological activity. In animals, cells often exist in the free state or in combination with proteins.
D-biotin nutrition mechanism
D-Biotin has both bound and free forms. The bound biotin cannot be used directly by the animal and must be decomposed by the biotin-degrading enzymes of the intestine to release free biotin before it can be used by animals. Biotin is well absorbed in the small intestine and is absorbed in intact molecules in the 1/3 to 1/2 segments of the small intestine. The porcine stomach cannot absorb biotin, the small intestine is the main site of absorption, and the colon can also absorb biotin, while chickens absorb biotin mainly in the small intestine. Almost all cells have biotin and the content in the liver and kidneys is relatively high.
The content of biotin is related to the biochemical effects of cells. Isotope markers indicated that the content of biotin in the proximal epithelial cells, hepatocytes, intestinal villus epithelial cells, and adipocytes of the kidneys is high, while the contents in some rapidly proliferating cells such as renal cortical cells, bone marrow cells, and lymphocytes are low. When pigs are fed diets supplemented with biotin, the concentration of biotin will increase in the liver, kidneys and heart. When the D-biotin intake is more than necessary, the exceeded will are excreted through the urine. Unabsorbed biotin in feed will be discharged from feces.
D-biotin Function
D-Biotin is a coenzyme component of sacetyl-CoA carboxylase, pyruvate carboxylase, propionyl-CoA carboxylase, and 3-methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase four carboxylase. It also play an important role in glucose, amino acid and fatty acid metabolism in animals, like in human beings.
D-Biotin and Carbohydrates metabolism: In gluconeogenesis, pyruvate carboxylase, which uses biotin as a coenzyme, is a key enzyme in pyruvic acid to produce butanion acid. Therefore, when the supplement of D-Biotin in the feed is insufficient, the glycogen will be quickly depleted or reduced, and hypoglycemia will occur. Especially, the glycogen stores in the chicks are relatively small and often leads to death.
D-Biotin and fat metabolism: In the process of fat metabolism, biotin acts as a coenzyme for acetyl-CoA carboxylase and catalyzes the formation of malonyl-CoA from acetyl-CoA. In the deficiency of biotin, abnormal lipid metabolism results in changes in the body’s fatty acid composition, reduced synthesis of saturated fatty acids, and increased synthesis of triacylglycerols, resulting in significant increases in lipids in the liver and kidneys.
Biotin and proteins, nucleic acids metabolism: biotin plays an important role in protein synthesis, amino acid decarboxylation, purine synthesis, carbamoyl transfer, and leucine and tryptophan catabolism, and is also required for the transfer and decarboxylation of many amino acids. Biotin not only participates in the carboxylase metabolic pathway, but also affects gene expression. The deficiency of biotin in animals will lead to slow cell proliferation, impaired immune function, and abnormal embryonic development.
Vitamin B7 D-Biotin Uses FAQ
Can you take D-Biotin while pregnant?
D-Biotin is considered safe during pregnancy and is available without prescription. D-Biotin supplement can avoid the deficiency as more Biotin needed during pregnancy. It is generally safe but better consult your doctor before taking any new supplement while pregnancy.
Can you take too much D-Biotin?
Better not take too much D-Biotin daily. D-Biotin is a water-soluble vitamin, your body does not store the excess quantity. This means if you take too much biotin than you need via supplementation, your body will likely release the extra biotin in your urine.
D-Biotin recommended daily intake
The U.S. Institute of Medicine recommended daily intake and how much D-Biotin can take as follows:
| Life Stage | Age | Males: (mcg/day) | Females: (mcg/day) |
| Infants | 0–6 months | 5 | 5 |
| Infants | 7–12 months | 6 | 6 |
| Children | 1–3 years | 8 | 8 |
| Children | 4–8 years | 12 | 12 |
| Children | 9–13 years | 20 | 20 |
| Adolescents | 14–18 years | 25 | 25 |
| Adults | 19 years and older | 30 | 30 |
| Pregnancy | all ages | – | 30 |
| Breast-feeding | all ages | – | 35 |
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) suggest for women and men over age 18, the Adequate Intake is set at 40 μg per day. The AI for pregnancy is 40 μg per day, and 45 μg per day during breastfeeding. For children ages 1–17 years, the AIs increase with age from 20 to 35 μg per day.
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biotin
How much D-Biotin do you need?
How much you need depending on your situation, your doctor might recommend a higher dose. Even at high levels, biotin appears to be fairly safe. Researchers don’t know at what dosage biotin might start to pose health risks.
How much D-Biotin is too much?
200mg is too much. There are currently no published medical reports of biotin toxicity. Although according to the National Institute of Health, doses as high as 200 mg have been used without significant adverse effects. However, the National Institute of Health recommends that higher doses than the recommended AI should not be taken without medical supervision.
How much D-Biotin is safe?
The recommended daily intake of Biotin is 30 micrograms (0.03 mg). For most individuals, supplementation is not necessary to avoid deficiency as biotin is found in most commonly natural foods.
However, biotin supplementation in large doses, sometimes over 50 times the recommended daily intake, is very popular to support hair, nail and skin growth. While evidence is mixed regarding just how well biotin works in this regard, studies show that biotin is extremely safe, even in large doses, and is unlikely to cause serious adverse events.
Reference: https://www.pharmacistanswers.com/questions/can-you-too-much-biotin
How much D-Biotin daily for hair growth?
Keratin is a basic protein that makes up your hair, skin, and nails. It’s clear that biotin improves your body’s keratin infrastructure. But beyond that, researchers aren’t really sure what biotin’s role in hair or skincare is.
Research on the effects of biotin on hair growth is sparse. To date, there’s only limited evidence to suggest that increased biotin intake may help promote hair growth.
Reference: https://www.healthline.com/health/biotin-hair-growth
How much D-Biotin should i take for hair loss?
The current recommended dosage of Biotin in Europe is set at 50 mcg/day. And how much Biotin should you take for hair growth may be some sort of a confusion regarding reference values because Europe and the USA have different numbers. The average intake from foods that contain Biotin in most western populations is about 35–70 mcg/day, showing that most people in these countries consume sufficient amounts of Biotin.
Biotin is a popular supplement for hair, skin, and fingernails, though there is little evidence to suggest that taking biotin supplements can stop hair loss or stimulate hair or nail growth. Similarly, using biotin shampoo or other hair products is unlikely to produce any benefit. There is some evidence that taking biotin supplements with other medications may help control hair loss that’s associated with childhood alopecia.
Reference: https://www.everydayhealth.com/drugs/biotin
D-Biotin nutrition facts
| Nutrition Facts | |
|---|---|
| 100g D-Biotin | |
| Calories 0 | Calories from Fat 0(%) |
| % Daily Value * | |
| Total Fat 0g | – |
| Sodium 0mg | 0% |
| Carbohydrates 0g | – |
| Net carbs 0g | – |
| Fiber 0g | 0% |
| Protein 0g | |
| Vitamins and minerals | |
| Vitamin A 0μg | 0% |
| Vitamin C 0mg | 0% |
| Calcium 0mg | 0% |
| Iron 0mg | 0% |
| Fatty acids | |
| Amino acids | |
Is D-biotin only for females?
Obviously not, D-Biotin is both for females and males. Biotin is a B Vitamin which is recommended for men and women.
Vitamin B7 D-Biotin Function and Benefits
What is the function of D-Biotin in body?
- Convert food into glucose, which is used to produce energy
- Produce fatty acids and amino acids (the building blocks of protein)
- Activate protein/amino acid metabolism in the hair roots and fingernail cells.
What is the benefits of D-Biotin in body?
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), which provides scientific advice to policy makers, has confirmed that clear health benefits have been established for the dietary intake of biotin (vitamin B7) in contributing to:
- Normal macronutrient metabolism
- Normal energy yielding metabolism
- The maintenance of normal skin and mucous membranes
- The normal function of the nervous system
- The maintenance of normal hair
- Normal psychological functions.
Vitamin B7 D-Biotin Side effects
Biotin is a safe and nontoxic vitamin. It has not been associated with any serious side effects, even in large doses. The FDA reports that biotin is safe and well tolerated when taken by mouth in recommended doses. But some have the opinion that Biotin may have side effects and it is bad for us:
- Acne
- Allergic Reactions
- Effects During Pregnancy
- Frequency Of Urination
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Increase Blood Glucose Levels
- Drug Interactions
- Eosinophilic Pleuropericardial Effusion
- Acute Respiratory Problems
Reference: http://www.stylecraze.com/articles/serious-side-effects-of-biotin-on-your-health
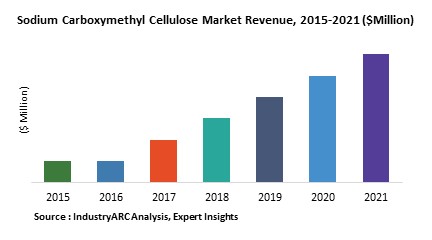
Vitamin B7 D-Biotin market
The major drivers for the global biotin market are the increasing uses of biotin in food, feed and cosmetics products. This is majorly due to increasing awareness regarding benefits associated with biotin such as improved skin, food conversion into glucose, production of fatty acids and activating production of protein/amino acid metabolism in the fingernail cells and hair roots. Also, biotin supplements boosts hair and nail growth making nails thicker and less brittle, therefore increasing the usage of products with D-Biotin.
Vitamins Market in Feed
Vitamins are a huge family. There are dozens of vitamins known so far, which can be broadly divided into fat-soluble and water-soluble categories: fat-soluble vitamins including Vitamin A, Vitamin D,Vitamin E,Vitamin K and etc.; water-soluble vitamins including B vitamins, like Vitamin B1, Vitamin B2, Vitamin B5, Vitamin B6, Vitamin B12 and Vitamin C, Vitamin B7 (D-Biotin) , Vitamin B3, Folic acid, Choline and so on. The demand of Vitamin A, Vitamin E and Vitamin C are very large and the global annual demand is around 10,000 ton for each vitamin.
Vitamin B belongs to small demand category and the market demand in the vitamin family is small if compared with Vitamin A, Vitamin E and Vitamin C, like D- Biotin and Folic acid. The annual demand is in the 100 tons and 1000 tons respectively.
From our statistics, 45% of Vitamins are used as feed additives, and 30% in pharmaceutical & cosmetics and 25% in food and beverages. Except Vitamin B12, VitaminB1, inositol, Vitamin C, and other few varieties, more than 70% of the other Vitamins used as feed additives. And 75% of D-Biotin in the market are used in feed industry.
The market demand of feed additives will grow. Whether it is the expansion of population or the upgrading of food structure, the development of animal husbandry and raising the output level of animal husbandry will provide more fleshy for humans under conditions of limited and difficult to reverse cultivated land resources. Therefore, in the long run, the feed additive industry will continue to maintain growth. And the market of D-Biotin will also increase.
Vitamins Market in Food
Vitamins are more commonly used in functional beverages in the market. These beverages are based on water and are prepared by adding amino acids, Taurine, Caffeine, electrolytes, vitamins and other natural nutrients and adjusting their composition and content ratio. According to the nutritional needs of certain special populations, the functional drinks like sports drinks, nutrient drinks, and other specialty beverages. According to calculations, the growth rate of vitamin application & use in the food and beverage market in recent years (10%-15%) is faster than that of medical cosmetics (3%-5%) and feed additives (1%-2%). With the benefit from the rapid growth of functional beverage market, the market demand of Nicotinamide, Calcium pantothenate, B1, B6, VC and other vitamin is increasing.
Vitamin B7 D-Biotin manufacturers and price trend in 2017
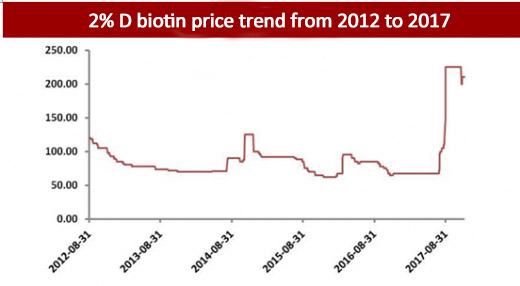
China is the big food and feed grade D-Biotin manufacturers and export country in the world. China manufactures’ market takes around 90%.
Today’s price
Updated on 2018/05/26: Now the price for feed grade 2% D-Biotin is around RMB54/kg, the price in January was around RMB190/kg, it decreased around 75%.
The price of Pure D-Biotin was around USD 1900/kg to USD2200/kg at high level in 2017.
Where to buy Vitamin B7 D-Biotin?
You can buy food or feed grade Vitamin B7 D-Biotin from us, Specification complies with BP/USP/EP/JP/FCC standard. As a D-Biotin manufacturer and supplier, we sell D-biotin pure; 10% D-Biotin food grade (Maltodextrin as carrier); 2% D-Biotin feed grade (Maltodextrin as carrier) and 1% D-Biotin feed grade (Dicalcium Phosphate as carrier)
We’re committed to the quality and safety of our ingredients. We know that our customers expect us to use only the highest quality food additives & ingredients with better price, and we do everything we can to satisfy those expectations.
Usage: feed additives, food additives, cosmetic ingredients and pharmaceuticals
Specification:
- D-biotin pure
- 10% D-Biotin food grade (Maltodextrin as carrier)
- 2% D-Biotin feed grade (Maltodextrin as carrier)
- 1% D-Biotin feed grade (Dicalcium Phosphate as carrier)
If you have any other questions, please email us through: info@foodsweeteners.com